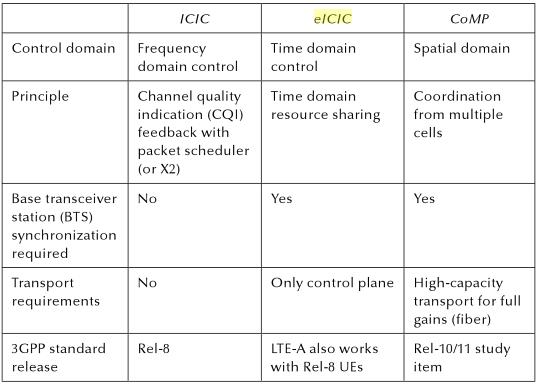
eICIC
(enhanced Inter-cell interference coordination)
·
eICIC
introduced in 3GPP release 10
·
eICIC
introduced to deal interference issues
in Heterogeneous Networks (HetNet)
·
eICIC
mitigates interference on traffic and control channels
·
eICIC
uses power, frequency and also time domain to mitigate intra frequency interference in heterogeneous networks
ICIC
technology evolution
In time domain
approach, a subframe can take MBSFN subframe approach.
MBSFN
subframe
·
MBSFN subframes and almost blank subframes that we
mentioned previously could be used to reduce interference to the co-channel
PDCCH in the other cell layer.
·
The macrocell and picocell can configure their MBSFN
and almost blank subframes in a cooperative manner in the time domain. For
MBSFN, the macrocell configures subframe N as an MBSFN subframe with only one
OFDM symbol used for the control region, while the picocell configures this
subframe as a normal subframe.
·
Thus, only one OFDM symbol in the control region at
the picocell would suffer the improved compared with the situation where all of
the three OFDM symbols are the Victims.
·
The almost
blank subframe (ABS) refers to the subframe that carries only the CRS in the
whole subframe region. Similar to the previous MBSFN, the interference of the
control channel could be alleviated. For example, we assume that the eNBI sends
the ABS pattern and the RNTP, UL HII (high interference indicator), and UL 01
(overload indicator) to the eNB2.
· We also assume that the DL subframe n is configured as an ABS. The ABS may have no other signals that are transmitted in ABSs except the CRS.
· We also assume that the DL subframe n is configured as an ABS. The ABS may have no other signals that are transmitted in ABSs except the CRS.
·
If the primary
synchronization signal (PSS), secondary synchronization signal (SSS), physical
broadcast channel (PBCH), system information block (SIB) 1, paging, and the
positioning reference signal (PRS) coincide with an ABS.
·
They will be transmitted in the ABS. In CoMP
scenarios, an aggressor cell informs a victim cell of certain ABSs in a
time-domain manner, and based on this information the victim cell can perform
appropriate user scheduling with RRC signalling to UEs for related RRM and CSI
measurements .
·
In the DL subframe, which is configured as an ABS by
eNBI, eNB2 can do PDSCH scheduling without being concerned with the
interference from eNBI regardless of the RNTP message.
·
It is worth
mentioning that the performance of the victim PDCCH and PDSCH could be improved
further if the UE is enabled with the capability to detect and cancel the neighbour
cell's CRS.
·
Interference from the macro, and the PDCCH performance
at the picocell could be another method of decreasing the interference is power
reduction or muting on the portion of symbols of the macrocell that overlapped
the control region of the picocell by scheduling and power control.
·
From the
previous discussion we can see that Rel-8 and Rel-9 frequency domain ICIC and
LTE-A time domain ICIC can coexist.
·
Each eNB can send both Rel-8 and Rel-9 and LTE-A ICIC
messages to its neighbouring cell. Further, possible LTE-A eICIC methods include
space domain coordination, network power control, network interference
cancellation, network coding, network MIMO, and net-work beam-forming, which
means an aggressor cell informs a victim cell of certain kinds of network
information in a space, time, code, or frequency domain manner, so as to be utilized
at a victim cell for appropriate avoidance schemes.

No comments:
Post a Comment